Introduction to Terraform
Introduction
• Started 2014
• Terraform is the infrastructure as code offering from HashiCorp.
• Single declarative language instead of configuration through various dashboards.
• HCL - HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL)
• HitashiCorp makes Vagrant, Packer, Vault, Consul, Nomad
• Two versions, Cloud (Open Source) and Enterprise (Paid For)
• Enterprise has better auditing and more templates.
• Can run, Amazon AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Oracle, Alibaba Cloud
• IT is commonly misunderstood that you can run a file against multi clouds verbatim i.e. without any modifications.
Advantages
• Easily repeatable
• Easily readable
• Operational certainty with "terraform plan"
• Standardised environment builds
• Quickly provisioned development environments
• Disaster recovery
Complimentary Technologies
• Ansible
• Chef
• Puppet
• SaltStack
• Packer = You create a stack (like a container) that you deploy to a server. Docker changes the server (you run it on the server)
• Docker = Containers
• Kubernetes = Open Source Docker Container Manager
• Nomad = HashiCorp version of Kubernetes (provisions containers)
HCL Files
• Split into two (Provider and Resource)
• The provider block configures the named provider such as AWS, Azure,
• The resource block defines a piece of infrastructure. A resource might be a physical component such as an EC2 instance, or it can be a logical resource such as a Heroku application.
Provider
Go to terraform.io to see the list of providers.
Current List
• ACME
• Akamai
• Alibaba Cloud
• Archive
• Arukas
• Auth0
• Avi Vantage
• Aviatrix
• AWS
• Azure
• Azure Active Directory
• Azure Stack
• A10 Networks
• BaiduCloud
• Bitbucket
• Brightbox
• CenturyLinkCloud
• Check Point
• Chef
• CherryServers
• Circonus
• Cisco ASA
• Cisco ACI
• Cloudflare
• Cloud-init
• CloudScale.ch
• CloudStack
• Cobbler
• Cohesity
• Constellix
• Consul
• Datadog
• DigitalOcean
• DNS
• DNSimple
• DNSMadeEasy
• Docker
• Dome9
• Dyn
• EnterpriseCloud
• Exoscale
• External
• F5 BIG-IP
• Fastly
• FlexibleEngine
• FortiOS
• Genymotion
• GitHub
• GitLab
• Google Cloud Platform
• Grafana
• Gridscale
• Hedvig
• Helm
• Heroku
• Hetzner Cloud
• HTTP
• HuaweiCloud
• HuaweiCloudStack
• Icinga2
• Ignition
• Incapsula
• InfluxDB
• Infoblox
• JDCloud
• KingsoftCloud
• Kubernetes
• Lacework
• LaunchDarkly
• Librato
• Linode
• Local
• Logentries
• LogicMonitor
• Mailgun
• MetalCloud
• MongoDB Atlas
• MySQL
• Naver Cloud
• Netlify
• New Relic
• Nomad
• NS1
• Null
• Nutanix
• 1&1
• Okta
• Okta Advanced Server Access
• OpenNebula
• OpenStack
• OpenTelekomCloud
• OpsGenie
• Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
• Oracle Cloud Platform
• Oracle Public Cloud
• OVH
• Packet
• PagerDuty
• Palo Alto Networks
• PostgreSQL
• PowerDNS
• ProfitBricks
• Pureport
• RabbitMQ
• Rancher
• Rancher2
• Random
• RightScale
• Rubrik
• Rundeck
• RunScope
• Scaleway
• Selectel
• SignalFx
• Skytap
• SoftLayer
• Spotinst
• StackPath
• StatusCake
• Sumo Logic
• TelefonicaOpenCloud
• Template
• TencentCloud
• Terraform
• Terraform Cloud
• Time
• TLS
• Triton
• Turbot
• UCloud
• UltraDNS
• Vault
• Venafi
• VMware Cloud
• VMware NSX-T
• VMware vCloud Director
• VMware vRA7
• VMware vSphere
• Vultr
• Wavefront
• Yandex
Declarative vs Procedural
Terraform is a declarative type language.
Declarative
Define how the end-state should look
There shall be a load balancer in front of a pool of 3 servers
Procedural
Perform set of actions to create an end state
Installing Terraform
https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
We can use Homebrew or Chocolatey on Windows to install Terraform. Alternatively, we can perform a manual installation with a binary package.
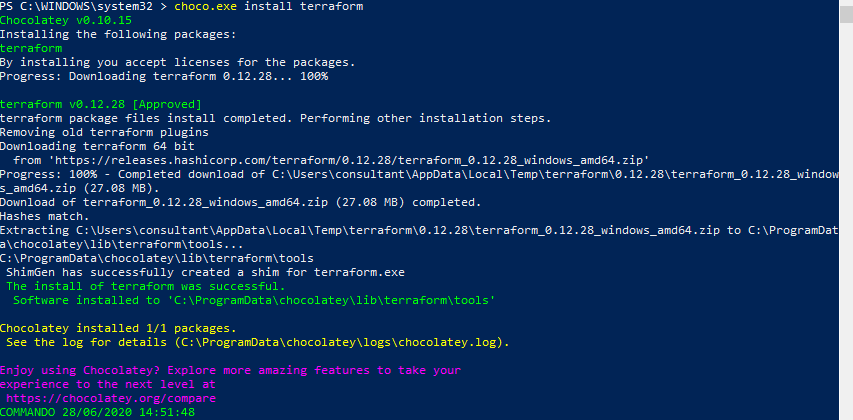
Chocolatey
Run the following after installing Chocolatey
choco install terraform
terraform --help
Example Output
Manual
For manual installation, you need to download the binary and add the location to your system path.
Building Infrastructure
• The set of files used to deploy your infrastructure is called a 'configuration'
The prerequisite to run the below is an AWS Account and the AWS CLI installed.
mkdir learn-terraform-aws-instance
cd learn-terraform-aws-instance
nano example.tf
provider "aws" {
profile = "default"
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-2757f631"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
terraform init
terraform apply
At this point, you will be prompted as below
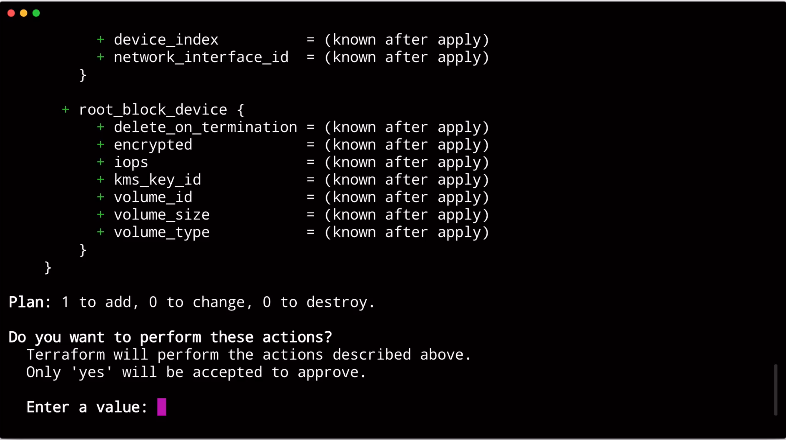
At this point you can cancel out and it will have no effect, alternatively you can proceed. Terraform will create your infrastructure.
You can run the following to see your infrastructure.
terraform show
When you have finished you may run the following to tear down the infrastructure.
terraform destroy
Coding
• Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ, Eclipse, all have support for terraform.
• Lists are the same as arrays in Php or Dictionary in Python
• Sets are like Tuples in Python.
We can set variables
variable "location" {
description = "Name of the Azure region to create resources in"
default = "westus2"
type = string
}
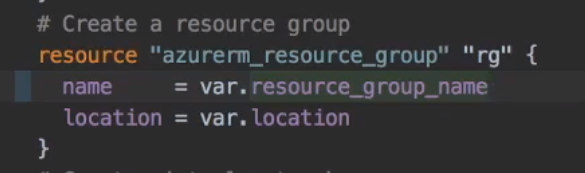
We can use variables
resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" {
name = "tf-variables-rg"
location = var.location
}
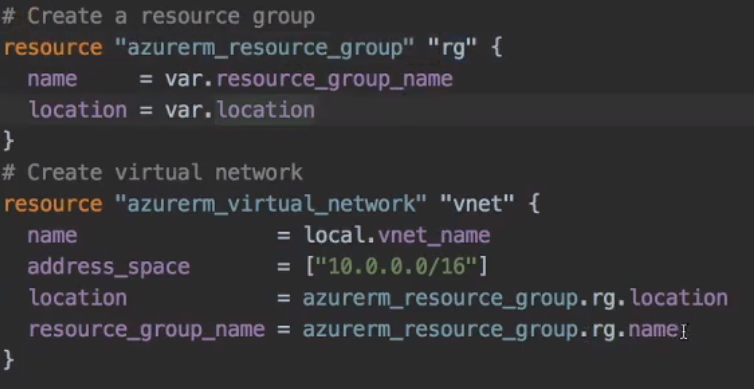
Cross References
Changing Configuration
As you change Terraform configurations, Terraform builds an execution plan that only modifies what is necessary to reach your desired state.
Resources
Repo from Cybrary Trainer https://github.com/jleonelion/fundamentals-of-terraform
Terraform Releases https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/

