Encoding PowerShell
19 Apr 2022, 12:14 p.m.
13 Apr 2022, 4:34 p.m.
00:60 minutes

The use of the `-EncodedCommand` PowerShell parameter is typically used by Administrators to run complex scripts without having to worry about escaping characters. However, it is commonly used by adversaries to hide their code. While it also offers obfuscation, remember base64 encoding can be decoded, so this is only real protection against shoulder surfers or people not in possession of decoding software.
Encoding Powershell
One gotcha that typically catches people out is the fact that PowerShell command encoding requires you to convert to unicode characters first which are two bytes compared to ASCII. I often see juniors comparing the Base64 generated by the below commands with that of an online base64 encoder and then question why their outputs differ.
Compare this
[System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes('A')
With
[System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes('A')
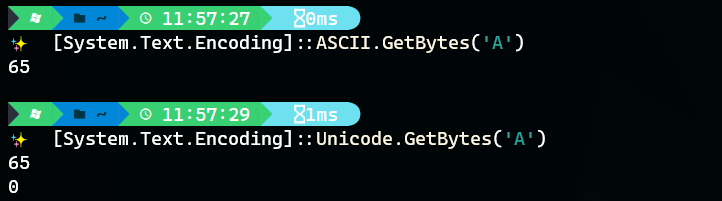
The manual method of encoding Powershell with no external libraries
$command = "net use; dir 'C:\Program Files\';ipconfig;ping 8.8.8.8"
$bytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($command)
$encodedCommand = [Convert]::ToBase64String($bytes)
powershell.exe -EncodedCommand $encodedCommand
Out-EncodedCommand cmdlet from Powersploit
Out-EncodedCommand -Path C:\cmds.txt -NonInteractive -NoProfile -EncodedOutput
Invoke-Encode cmdlet from Nishang
Invoke-Encode -DataToEncode c:\data.txt -OutCommandInvoke-Encode "net use; systeminfo" -OutCommandInvoke-Encode $commands -OutCommand
Invoke-Obfuscation cmdlet (https:.com-Obfuscation)
Import-Module C:\Powershell\Invoke-Obfuscation\Invoke-Obfuscation.psd1
Invoke-Obfuscation
SET SCRIPTBLOCK cmd 1; cmd 2; cmd3; cmd4
SET SCRIPTBLOCK Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem; systeminfo; Write-Host 'Finished'

